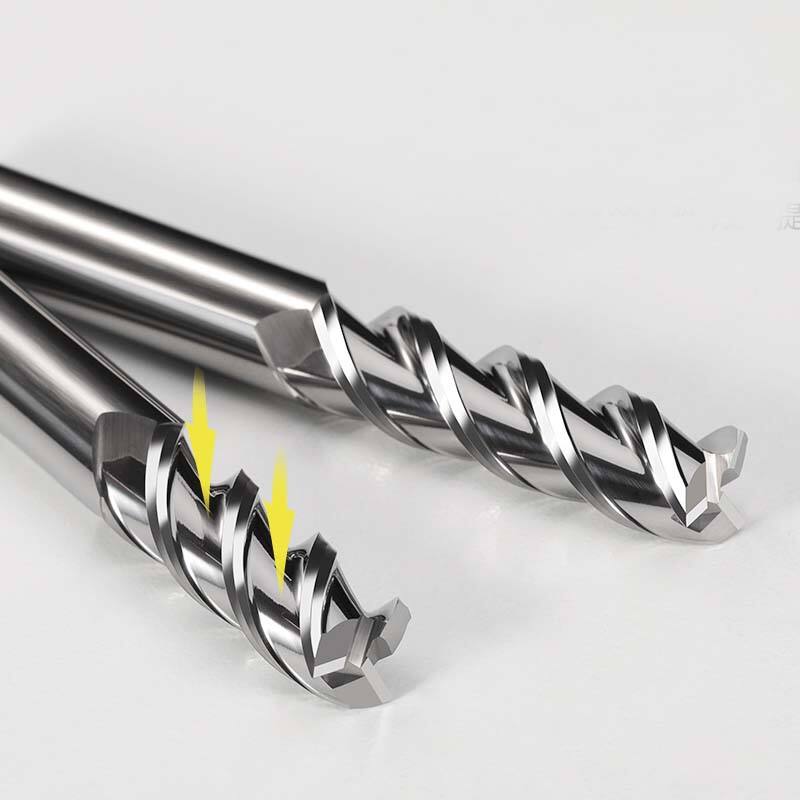
Analysis on the Causes of Wear of Damaged Hard Alloy Milling Knives
Formed hard alloy milling cutters are widely used due to their small shape tolerance. Due to the inability to directly replace the blade, most milling cutters are scrapped after bursting, greatly increasing processing costs.
1. Processing material properties
When cutting titanium alloy, due to the poor thermal conductivity of titanium alloy, the chips are easily adhered to the vicinity of the tool tip or formed into chip deposits, forming high-temperature zones on the front and rear cutting surfaces near the tool tip, resulting in the loss of tool hardness and increased wear. In continuous cutting under high temperature conditions, the bonding and fusion materials are subjected to subsequent processing impacts, and during the forced punching process, some tool materials are taken away, resulting in tool defects and damages. In addition, when the cutting temperature reaches above 600 ℃, a hardened hard layer will form on the surface of the part, which will have a strong wear effect on the tool. Titanium alloy has a low elastic modulus, large elastic deformation, and a large surface rebound near the back cutting surface, resulting in a large contact area between the machined surface and the back cutting surface and severe wear.
2. Normal wear and tear
In normal production and processing, severe blade wear occurs when the allowance for continuous milling of titanium alloy parts reaches 15mm-20mm. The efficiency of continuing milling is extremely low, and the surface finish of the machined parts is poor, which cannot meet production and quality requirements.
3. Improper operation
During the production and processing of titanium alloy castings, such as boxes and covers, improper clamping, improper cutting depth, excessive spindle speed, and insufficient cooling can lead to tool breakage, damage, and breakage. This type of defective milling cutter not only fails to perform effective milling, but also causes surface defects such as dents on the machining surface due to "gnawing" during the milling process, which not only affects the machining quality of the milling surface, but also leads to the scrapping of the machined parts in severe cases.
 EN
EN
 AR
AR
 BG
BG
 HR
HR
 CS
CS
 DA
DA
 NL
NL
 FI
FI
 FR
FR
 DE
DE
 EL
EL
 HI
HI
 IT
IT
 JA
JA
 KO
KO
 NO
NO
 PL
PL
 PT
PT
 RO
RO
 RU
RU
 ES
ES
 SV
SV
 CA
CA
 TL
TL
 IW
IW
 ID
ID
 LV
LV
 LT
LT
 SR
SR
 SK
SK
 SL
SL
 UK
UK
 VI
VI
 SQ
SQ
 ET
ET
 GL
GL
 HU
HU
 MT
MT
 TH
TH
 TR
TR








